What is a non admitted insurance carrier – What is a non-admitted insurance carrier? These entities operate outside the traditional regulatory framework of admitted insurers, offering unique advantages and disadvantages for both consumers and businesses. Understanding their characteristics, market access methods, and regulatory landscape is crucial for navigating this sector of the insurance industry.
Non-admitted carriers often specialize in niche markets or utilize innovative distribution strategies. They typically operate outside the state-level licensing requirements of admitted carriers, which can impact their accessibility and consumer protection measures. This difference in regulatory oversight presents both opportunities and risks.
Definition and Characteristics
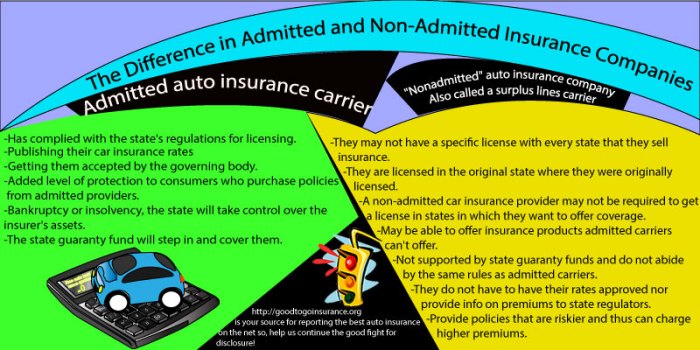
A non-admitted insurance carrier is an insurance company that does not hold a license to operate within a specific state’s regulatory framework. These entities, often operating across multiple states, may not have the same level of oversight as admitted carriers, leading to variations in their operational processes and customer protections. They typically rely on relationships with admitted carriers to facilitate their operations within a state.Non-admitted carriers operate outside the direct regulatory control of a particular state.
This differs significantly from admitted carriers, which are subject to state-specific licensing and regulations. Key distinctions lie in their ability to directly transact insurance within a state and the extent of consumer protections afforded by the state’s regulatory body.
Distinguishing Features of Non-Admitted Carriers
Non-admitted carriers are characterized by their lack of direct regulatory oversight within a particular state. Their operational processes and consumer protections are frequently influenced by the regulations of the states where they are admitted. This independence allows for a more flexible approach to market entry and operations but often comes with a different level of consumer safeguards.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
The legal and regulatory landscape governing non-admitted carriers is complex and varies significantly by state. States typically have laws and regulations governing the types of insurance products that non-admitted carriers can offer and the requirements for doing business within the state. These regulations are intended to protect consumers and ensure fair business practices. A crucial aspect involves the oversight of the admitted carriers with which the non-admitted carriers may partner.
Operating Procedures
Operating procedures for non-admitted carriers often involve collaborations with admitted carriers within the target states. These arrangements allow non-admitted carriers to access the local market without needing to comply with the direct regulatory requirements of that state. The specific procedures may include reinsurance agreements or reciprocal arrangements to facilitate insurance transactions within the target state.
Comparison of Admitted and Non-Admitted Carriers
| Characteristic | Admitted Carrier | Non-Admitted Carrier |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing Requirements | Must meet specific licensing requirements set by the state. | Typically does not hold a license in the state, relying on partnerships with admitted carriers. |
| Market Access | Can directly transact insurance within the state. | Access to the market often facilitated through agreements with admitted carriers. |
| Regulatory Oversight | Subjected to direct state regulatory oversight. | Subject to varying degrees of oversight, often relying on the regulations of the states where they are admitted. |
Types and Examples
Navigating the intricate world of non-admitted insurance carriers requires understanding their diverse forms and the unique characteristics of each. These carriers play a crucial role in the insurance landscape, offering specialized coverage and unique business models that cater to specific market segments. Their operations differ significantly from admitted carriers, often due to their less stringent regulatory oversight and specialized expertise.Understanding the variety of non-admitted insurance carriers and their respective offerings provides valuable insights into the intricacies of the insurance market.
This includes exploring their distinct business models, target markets, and distribution channels, ultimately shedding light on the dynamic nature of this segment of the insurance industry.
Types of Non-Admitted Carriers
Non-admitted insurance carriers exhibit a wide range of structures and specializations. This diversity reflects the need for insurance products tailored to specific niches and market demands. Key types include surplus lines, reinsurance, and captive insurance companies.
Surplus Lines Carriers
Surplus lines insurance companies cater to high-risk or unusual insurance needs that admitted carriers often decline. This market segment often includes specialized policies, such as those for construction projects or high-value assets, and businesses with unusual or complex risks. They operate outside the standard market channels, often utilizing independent agents or brokers.
Reinsurance Carriers
Reinsurance carriers provide a critical function in the insurance industry, acting as a safety net for admitted carriers. They share the risk of large losses, enabling admitted carriers to manage their risk profiles effectively and offer coverage to a wider range of clients. Reinsurers often focus on specific types of risks, such as catastrophe insurance or certain types of commercial insurance.
This allows admitted carriers to maintain financial stability and provide coverage for larger, more significant claims.
Captive Insurance Companies
Captive insurance companies are established and controlled by a specific entity, such as a corporation, to manage its own risks. They often insure the company’s own assets, operations, or affiliated entities. This allows for cost savings and tailored risk management, as well as greater control over insurance policies and claim processes.
Examples of Insurance Products
Non-admitted carriers offer a wide range of insurance products. These products cater to various market segments and often address specific risk profiles not readily covered by admitted carriers.
- Commercial Property Insurance: Surplus lines insurers frequently offer coverage for high-value assets or properties with unique exposures, not typically covered by admitted carriers.
- Specialty Liability Insurance: Surplus lines carriers are frequently sought for specialized liability coverage for businesses operating in niche markets.
- Construction Insurance: These policies address the inherent risks of construction projects, including potential liability from accidents or property damage.
- Professional Liability Insurance: Specific types of professional liability insurance, such as those for architects or engineers, might be handled by surplus lines companies.
- Catastrophe Reinsurance: Reinsurance companies play a critical role in mitigating the financial impact of large-scale disasters.
Business Models of Non-Admitted Carriers
The business models of non-admitted carriers often differ from admitted carriers, reflecting their unique approach to risk management and coverage.
- Direct Marketing: Some carriers utilize direct marketing approaches to reach clients with targeted advertising.
- Brokerage Networks: Many non-admitted carriers rely on networks of independent agents or brokers to reach a wider customer base.
- Specialization: Some non-admitted carriers focus on a specific niche, such as construction or marine insurance, to gain expertise and market share.
Table of Non-Admitted Insurance Carriers
The table below highlights the key characteristics of various non-admitted insurance carriers.
| Carrier Type | Product Types | Target Market | Distribution Channels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surplus Lines | High-risk, specialty, and unusual risks | Businesses with unique or complex risks | Independent agents, brokers |
| Reinsurance | Catastrophe, commercial, and other specialized risks | Admitted carriers seeking risk transfer | Direct contracts with admitted carriers |
| Captive Insurance | Tailored to specific entity’s risks | Corporations, businesses, and other entities | Direct or through internal departments |
Challenges and Opportunities
Non-admitted carriers face unique challenges, often stemming from their regulatory environment and market positioning.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating regulatory compliance and licensing requirements can be complex and demanding for non-admitted carriers.
- Competition: Competition from both admitted and non-admitted carriers can be intense, particularly in the surplus lines market.
- Market Fluctuations: The insurance market is susceptible to fluctuations, impacting pricing and profitability.
- Specialized Expertise: Building and maintaining expertise in specific niche markets can be a considerable advantage.
Market Access and Distribution
Non-admitted insurance carriers, operating outside the regulatory framework of a specific state or jurisdiction, face unique challenges in accessing and distributing their products. Their strategies for market penetration often involve a blend of innovative approaches and careful navigation of compliance regulations. These carriers frequently rely on established distribution networks, while simultaneously adapting to evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements.
Methods of Market Access
Non-admitted carriers employ various strategies to enter markets and establish a presence. These include leveraging existing relationships with independent agents and brokerages, who often have extensive networks and established customer bases. Additionally, direct-to-consumer marketing, utilizing digital platforms and targeted advertising, is increasingly prevalent. These strategies, when effectively implemented, can provide significant market penetration without the need for state-specific licensing and associated regulatory burdens.
Distribution Channels
The distribution landscape for non-admitted carriers is dynamic and multifaceted. They leverage a variety of channels to connect with potential customers. This includes utilizing online platforms, social media marketing, and strategic partnerships with related industries. These channels offer a means to reach diverse customer segments, tailoring their messages and offerings to specific needs.
Customer Interaction
Non-admitted carriers interact with customers through a variety of methods, ensuring a seamless and efficient experience. Direct communication, often through dedicated websites and customer service channels, allows for personalized interaction. Furthermore, utilizing technology to facilitate quotes, applications, and policy management, streamlines the entire customer journey.
Distribution Channel Illustration
| Distribution Channel | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Platforms | Websites, mobile apps, and online marketplaces provide 24/7 access to product information and quotes. | Enhanced accessibility, broad reach, cost-effectiveness, and data-driven insights. | Requires significant investment in website development and maintenance, potential for security concerns, and reliance on digital literacy. |
| Independent Agents | Partnerships with licensed agents enable localized marketing and customer service. | Established relationships with clients, local expertise, and personalized service. | Potential for conflicts of interest, dependence on agent performance, and challenges in managing agent networks. |
| Brokerages | Collaborations with insurance brokerages allow access to a wider client base and specialized services. | Access to a diverse client portfolio, specialized expertise, and streamlined administrative processes. | Potential for high transaction costs, complexities in broker relationships, and challenges in managing client expectations. |
Marketing Strategies
Successful non-admitted carriers frequently utilize targeted marketing campaigns to connect with their desired customer base. These campaigns leverage data analysis to tailor messaging, identify specific customer needs, and promote products that address those needs. Utilizing social media platforms to reach specific demographics and build brand awareness are also critical components of successful marketing strategies. For example, a carrier targeting small business owners might focus on targeted ads on LinkedIn, while a carrier focusing on individuals might leverage social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
Navigating the intricate world of non-admitted insurance carriers necessitates a profound understanding of the regulatory environment. These entities operate outside the traditional admission processes of state insurance departments, requiring a distinct set of compliance measures to ensure consumer protection and market integrity. This section delves into the specific regulations and compliance requirements for non-admitted carriers, highlighting the potential risks and liabilities associated with non-compliance.The regulatory landscape for non-admitted insurance carriers is diverse, varying significantly based on the specific state and the type of insurance product offered.
These differences stem from the need to balance the interests of consumers with the competitive landscape, allowing for flexibility while maintaining essential protections.
Regulatory Environment
Non-admitted insurance carriers operate within a framework of state-specific regulations. These regulations often mandate specific requirements for licensing, financial solvency, and claims handling procedures. State insurance departments play a crucial role in overseeing these carriers and ensuring compliance with these mandates.
Compliance Requirements
Compliance with regulations is paramount for non-admitted carriers. This involves adhering to state-specific licensing requirements, maintaining adequate financial reserves, and adhering to established claims handling procedures. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in severe consequences.
Potential Risks and Liabilities
Non-compliance with regulatory requirements can lead to significant risks and liabilities for non-admitted carriers. These risks include fines, license suspension or revocation, legal action, and reputational damage. Moreover, violations can result in substantial financial penalties. Examples include substantial monetary fines levied for misrepresenting financial standing or for failing to comply with specific reporting requirements.
Common Regulatory Violations
Several common regulatory violations affect non-admitted carriers. These violations often involve misrepresenting financial strength, failing to comply with licensing procedures, improper claims handling practices, and inadequate consumer disclosure. A common example is failing to disclose material facts about the insurer’s financial status, leading to potential misrepresentation or deception.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies, such as state insurance departments, play a crucial role in overseeing non-admitted insurance carriers. These bodies monitor compliance with regulations, investigate potential violations, and take appropriate enforcement actions to ensure market integrity. They ensure fair practices and fair pricing. State insurance commissioners, through their departments, have the power to impose sanctions and penalties on non-admitted carriers for violations, promoting consumer protection.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Navigating the world of insurance carriers reveals a spectrum of choices, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these nuances is crucial for both consumers and businesses seeking the most suitable coverage. Non-admitted carriers, while often presenting a compelling cost-conscious option, come with specific limitations compared to their admitted counterparts. This section delves into the trade-offs associated with each type of carrier, illuminating the impact on consumer choice and market competitiveness.
Advantages of Non-Admitted Carriers
Non-admitted carriers frequently offer lower premiums due to their distinct operational structures and reduced regulatory burdens. This competitive pricing can be particularly attractive for individuals and businesses seeking cost-effective insurance solutions. Additionally, the streamlined approval processes sometimes associated with non-admitted carriers can expedite the insurance procurement process, making it a faster and more efficient option for certain situations.
Disadvantages of Non-Admitted Carriers
While non-admitted carriers can present a cost-effective option, they often come with limitations in terms of consumer protection. The lack of state-level oversight can potentially reduce the recourse available to policyholders in the event of a claim dispute. Further, consumers may have fewer options for filing grievances or resolving issues with the insurer, posing a significant drawback.
Advantages of Admitted Carriers
Admitted carriers, operating under the scrutiny of state regulatory bodies, often provide a higher degree of consumer protection. These carriers are subject to strict regulations, ensuring compliance with state laws and safeguarding policyholders’ rights. Their established presence within the insurance market also typically provides greater claim processing reliability and transparency.
Disadvantages of Admitted Carriers
Admitted carriers, despite their regulatory oversight, frequently have higher premiums compared to their non-admitted counterparts. This higher cost is a direct result of the regulatory compliance and operational expenditures associated with maintaining state-level licenses and adhering to mandated reporting requirements. The broader regulatory environment can also result in slower processing times for claims and applications.
Comparison of Non-Admitted and Admitted Carriers
| Feature | Non-Admitted Carrier | Admitted Carrier |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally lower premiums | Generally higher premiums |
| Coverage Options | Potentially limited selection, often focusing on specific types of coverage | Wider range of coverage options, often tailored to diverse needs |
| Customer Service | Potentially less readily accessible customer service, with varied levels of support | Typically more established customer service channels and support resources |
Impact on Consumer Choice and Market Competition
The contrasting advantages and disadvantages of non-admitted and admitted carriers significantly impact consumer choice. Consumers often prioritize cost-effectiveness, leading to a higher demand for non-admitted carriers. However, this preference is frequently tempered by concerns about consumer protection. The presence of both types of carriers fuels market competition, driving innovation and ultimately influencing the pricing and service offerings within the insurance industry.
The availability of both options allows consumers to select the best fit for their specific needs and risk tolerance. For example, businesses with stringent compliance requirements might opt for admitted carriers, while those prioritizing cost-effectiveness might consider non-admitted ones.
A non-admitted insurance carrier operates outside the established regulatory framework, often offering unique coverage options. Their operations, while sometimes a bit unconventional, can be contrasted with the meticulous processes found in the study of food and culture, as explored in food and culture 7th edition. Ultimately, a non-admitted carrier’s status often reflects a different approach to the insurance landscape.
Consumer Protection and Rights: What Is A Non Admitted Insurance Carrier
Navigating the world of insurance can be complex, especially when dealing with non-admitted carriers. Understanding the consumer protections in place is crucial for ensuring fair treatment and recourse in case of issues. This section delves into the safeguards designed to shield consumers from potential harm and Artikels the procedures for resolving disputes.Consumer protection measures for non-admitted insurance carriers are generally less comprehensive compared to admitted carriers.
A non-admitted insurance carrier operates outside the established regulatory framework, often offering competitive rates. This can be a compelling choice, especially when considering a front porch for colonial house, where meticulous attention to detail and cost-effectiveness are paramount. However, understanding the nuances of non-admitted carriers is crucial for making informed decisions, as their practices may differ from those of admitted insurers.
This stems from the fact that non-admitted carriers often operate outside the traditional regulatory frameworks and oversight mechanisms that admitted carriers are subject to. Despite this difference, safeguards exist to protect consumers from exploitation and ensure a degree of fairness.
Consumer Protection Measures
The effectiveness of consumer protection hinges on the specific state and jurisdiction. While uniform standards are not always present, the overarching goal is to balance the needs of consumers with the realities of the insurance market. The measures in place vary, but typically include regulations regarding policy transparency, claims handling procedures, and dispute resolution mechanisms. These regulations are designed to ensure that consumers are not unfairly disadvantaged.
Consumer Rights When Dealing with Non-Admitted Carriers
Consumers dealing with non-admitted carriers have rights similar to those interacting with admitted carriers, albeit with potential variations depending on the jurisdiction. These rights often include the right to clear and concise policy terms, fair and timely claims processing, and a clear avenue for resolving disputes. Consumers should be aware of these rights to effectively safeguard their interests.
Specific rights can differ depending on state laws.
Procedures for Resolving Disputes, What is a non admitted insurance carrier
Dispute resolution procedures for non-admitted carriers typically involve a multi-step process, starting with internal complaint mechanisms. If these internal mechanisms prove insufficient, consumers may be able to escalate the dispute to state regulatory bodies or courts. This escalation pathway ensures a clear path to redress, though the exact steps and timeframes can differ from state to state. The process aims to be fair and equitable for both the consumer and the carrier.
Mechanisms for Investigating Consumer Complaints
State insurance departments often have established mechanisms for investigating consumer complaints against non-admitted carriers. These investigations can involve examining policy documents, interviewing parties involved, and reviewing claims handling processes. The goal is to determine whether the carrier has acted in accordance with state regulations and industry best practices. This ensures the protection of consumer interests.
Seeking Redress for Issues with Non-Admitted Carriers
If a consumer experiences issues with a non-admitted carrier, several avenues for redress are available. These may include filing a complaint with the state insurance department, pursuing arbitration, or filing a lawsuit. The choice of recourse often depends on the nature and severity of the issue, along with the specific state laws governing the dispute. Consumers should thoroughly research their options and consult with legal counsel if needed.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The non-admitted insurance market, often operating outside the traditional regulatory framework, is experiencing a period of dynamic evolution. This sector is increasingly adapting to changing consumer demands, technological advancements, and evolving regulatory landscapes. Understanding these trends is crucial for both carriers and stakeholders to navigate the complexities of this evolving marketplace.
Current Trends in the Non-Admitted Market
The non-admitted insurance market is characterized by a diverse range of players, from specialized niche providers to established companies seeking alternative distribution channels. Key trends include a growing focus on specific risk segments, such as professional liability or specialty lines. This specialization allows carriers to offer highly tailored coverage solutions, often meeting unmet needs in the market. Furthermore, there’s a noticeable shift towards digital platforms and online distribution channels.
This facilitates greater accessibility and efficiency in the sales process. Moreover, the integration of technology, like sophisticated risk assessment models, is becoming prevalent.
Future Outlook for Non-Admitted Carriers
The future outlook for non-admitted carriers hinges on their ability to adapt to evolving regulatory pressures, technological advancements, and the shifting competitive landscape. Increased regulatory scrutiny in some jurisdictions is likely to impact the operations of certain carriers, requiring adherence to stricter compliance standards. The emergence of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, is anticipated to transform risk assessment and claims processing, potentially leading to more accurate pricing and faster claim resolutions.
Moreover, the ongoing need for greater transparency and consumer protection will influence the strategies of non-admitted carriers.
Potential Impacts of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are poised to significantly reshape the non-admitted insurance industry. For instance, AI-powered risk assessment tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential risks with greater accuracy, leading to more precise pricing models. Furthermore, automated claims processing systems can expedite the claims resolution process, enhancing customer satisfaction. The use of blockchain technology could also improve the security and transparency of transactions within the industry.
These advancements could potentially reduce operational costs, improve efficiency, and offer more competitive pricing for consumers.
Innovative Approaches by Non-Admitted Carriers
Several non-admitted carriers are adopting innovative approaches to meet the demands of the evolving marketplace. Examples include partnering with technology platforms to enhance distribution channels, utilizing data analytics to refine risk assessment, and developing specialized products to cater to specific market segments. Furthermore, some carriers are experimenting with alternative distribution models, such as utilizing social media and online marketplaces to reach new customer segments.
These strategies aim to create competitive advantages in a dynamic market environment.
Challenges and Opportunities for Non-Admitted Carriers
Non-admitted carriers face a unique set of challenges in the future, including navigating complex regulatory landscapes, maintaining compliance with varying state regulations, and adapting to evolving consumer expectations. However, these challenges also present opportunities. The ability to tailor coverage to niche markets and offer competitive pricing models can be advantageous. Furthermore, leveraging technology to streamline operations and enhance efficiency can position non-admitted carriers for success.
The key will be to adopt innovative strategies while maintaining a focus on ethical and responsible business practices.
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, non-admitted insurance carriers offer a distinct alternative to traditional insurance providers. Their operational flexibility and targeted market approaches present unique opportunities, but consumers should be aware of the varying levels of consumer protection and regulatory oversight. A thorough understanding of their advantages, disadvantages, and regulatory landscape is crucial for informed decision-making.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the key differences between non-admitted and admitted carriers?
Admitted carriers are licensed and regulated within a specific state’s insurance framework, while non-admitted carriers operate outside those regulations. This difference affects licensing requirements, market access, and regulatory oversight.
What are the common distribution channels for non-admitted carriers?
Non-admitted carriers often utilize independent agents, brokerages, and online platforms to reach customers. Direct sales to businesses may also be employed.
What are the potential risks for consumers when dealing with non-admitted carriers?
Consumers may encounter limited access to state-level consumer protection resources, and dispute resolution processes might differ from those of admitted carriers. Understanding the specific protections offered is crucial.
What are the advantages of using a non-admitted carrier?
Non-admitted carriers may offer specialized products, more flexible coverage options, or potentially lower premiums. However, these are often balanced against the potential for reduced consumer protection.
